15 Miraculous AI Agent Strategies for Code Generation in 2026

Master 15 proven strategies to configure AI coding agents like Claude Code for better output. Includes CLAUDE.md examples, ESLint rules, and MCP workflows.
While I was configuring Claude Code for a new project the other day, I realized something that changed how I think about AI coding assistants entirely. The AI wasn't generating bad code because it was "dumb"—it was generating mediocre code because I hadn't given it the right operating instructions.
Here's a stat that blew my mind: at Anthropic, engineers adopted Claude Code so heavily that ~90% of the code for Claude Code is written by Claude Code itself. Yet, as Addy Osmani points out, using LLMs for programming is "difficult and unintuitive"—getting great results requires learning new patterns.
The difference between mediocre and miraculous AI output is 100% about configuration and communication. These 15 strategies are the playbook I've developed over months of working with AI agents daily. If you've been struggling to get consistent, high-quality code from your AI assistant, this post will change that.
Let's dive in.
1. Enforce Imports and Composition with ESLint
I noticed something frustrating early on: AI agents love reinventing the wheel. They'll write custom date formatting functions instead of using date-fns, or create inline utility helpers instead of importing battle-tested libraries.

The Problem: AI generates inline utility functions instead of using proven libraries, leading to bugs and inconsistency.
The Solution:
// eslint.config.js (flat config)
export default [
{
rules: {
'no-restricted-syntax': [
'error',
{
selector: 'CallExpression[callee.property.name="forEach"]',
message: 'Prefer lodash/forEach or for...of for complex iterations',
},
{
selector: 'NewExpression[callee.name="Date"]',
message:
'Use date-fns for date manipulation. Import: import { format } from "date-fns"',
},
],
},
},
]Why This Works: AI agents treat lint errors as hard constraints. When ESLint errors on new Date(), the AI will automatically refactor to use date-fns. I cannot stress this enough—lint rules are your first line of defense against AI anti-patterns.
I wrote more about enforcing AI agents to use specific patterns in a previous post.
2. Ask the AI What Confuses Them
This one sounds strange, but stay with me. We assume AI understands context it doesn't. By explicitly asking the AI to verbalize its understanding, we catch misalignments before code is written.
The Problem: AI makes wrong assumptions silently, leading to wasted iterations.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md
When starting any non-trivial task:
1. State what you understand the task to be
2. List what context is missing or unclear
3. Declare assumptions you're making
Example output format:
"I understand this as: [summary]. Missing context: [gaps]. Assuming: [assumptions]."Why This Works: This forces externalization of the AI's "thought process." You'll catch gaps before a single line of code is written. Trust me—this saves hours of back-and-forth.
3. Force Context7 Before Code Generation
This strategy alone probably saves me 30 minutes per day. AI models have stale training data. When you're using React 19, Next.js 15, or Tailwind 4, the AI will hallucinate APIs that don't exist.
The Problem: AI hallucinates APIs from outdated training data.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md
**Always use context7 when:**
- Starting any coding task involving external libraries
- Before generating code using library APIs
- When debugging library-related issues
Workflow:
1. Call `resolve-library-id` to get current version ID
2. Call `get-library-docs` with relevant topic filter
3. THEN write code based on fresh documentation
Never rely on training data for: React 19, Next.js 15, Tailwind 4, or any library updated in 2024+Why This Works: Context7 injects up-to-date documentation directly into the AI's context window. No more hallucinated useServerAction hooks that don't exist.
4. Instruct Clarifying Questions in CLAUDE.md
Boy, not everything in life goes in our favor—especially when vague requirements lead to wrong implementations. AI agents default to "just do something" mode, which often means wrong assumptions.
The Problem: AI makes silent assumptions instead of asking.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Clarification Protocol
When requirements are ambiguous, ask BEFORE coding:
- "Add authentication" → OAuth? JWT? Session? Magic link?
- "Make it performant" → What's baseline? Target latency?
- "Handle errors" → User-facing? Logging only? Recovery?
Format: Present 2-3 options with trade-offs, let user choose.Why This Works: Explicit instruction to ask questions overrides the AI's default "be helpful and just do it" behavior. You'll get questions like "Should this use JWT with refresh tokens or session cookies? Here are the trade-offs..." instead of a random implementation.
5. Expose Confidence Levels and Reasons
AI sounds confident even when guessing. This strategy makes uncertainty visible, so you know when to verify.
The Problem: AI sounds authoritative even when it's 50% sure.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Confidence Reporting
For technical decisions, report confidence:
- **HIGH (90%+)**: Documented best practice, matches codebase patterns
- **MEDIUM (60-89%)**: Reasonable approach, alternatives exist
- **LOW (<60%)**: Best guess, recommend verification
When confidence < 80%, state:
1. What would increase confidence
2. Risks with current approachExample Output:
"I'll use React Query for this (HIGH confidence—matches existing patterns in
src/hooks/). For the cache invalidation strategy, I'm at MEDIUM confidence—the docs suggeststaleTimeof 30s, but your use case might need real-time updates. Want me to check Context7 for current best practices?"
6. Declare Loaded Context at Session Start
This one's about transparency. You don't know what the AI "sees" in its context window, which makes debugging impossible.
The Problem: Users don't know what files are loaded, leading to confusion.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Context Transparency
At conversation start, report:
1. Files auto-loaded into context
2. Why each was loaded
3. Approximate token usage
When reading additional files, note context window impact.
Recommend fresh session when context exceeds 50% capacity.Why This Works: You'll know when to start fresh sessions and avoid "context pollution" where old, irrelevant code influences new generations.
7. Create Project-Scoped Rules Files
CLAUDE.md gets bloated fast. The solution? Modular rules files.
The Problem: One giant CLAUDE.md becomes unmanageable.
The Solution:
.claude/
├── CLAUDE.md # Project overview (keep <200 lines)
└── rules/
├── api-design.md # REST conventions, response formats
├── testing.md # Test patterns, mocking strategies
├── react-patterns.md # Component structure, hooks rules
├── database.md # Query patterns, migration format
└── security.md # Auth patterns, input validation
Each rule file should be 50-100 lines, focused on ONE domain. The AI loads relevant rules based on the task.
8. Ask if We Should Convert the Proposed Plan to a PRD or Keep as a Plan
Systematic implementation in phases catches phase-specific errors at their source instead of after the entire implementation is coded, making it difficult to track which phase the issue originated from.
The Problem: AI codes the entire implementation without phase-by-phase validation, making it hard to identify where phase-specific issues originated.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Phase-Based Implementation
When planning implementation:
1. Present the plan to the user
2. Ask: "Should we convert this to a PRD with phases, or keep as a plan?"
3. If PRD: Break into phases, validate each phase before next
4. If plan: Proceed with full implementation, but track phase context
Benefits: Errors caught at phase boundaries, easier debugging, clearer accountabilityWhy This Works: Phase-by-phase validation isolates errors to their source phase, making root cause analysis straightforward instead of debugging an already-completed implementation.
9. Enforce Reusable UI Components with ESLint
Stop scattered, inconsistent UI elements. Force all components to compose from a centralized UI library, making style changes instant across your entire codebase.
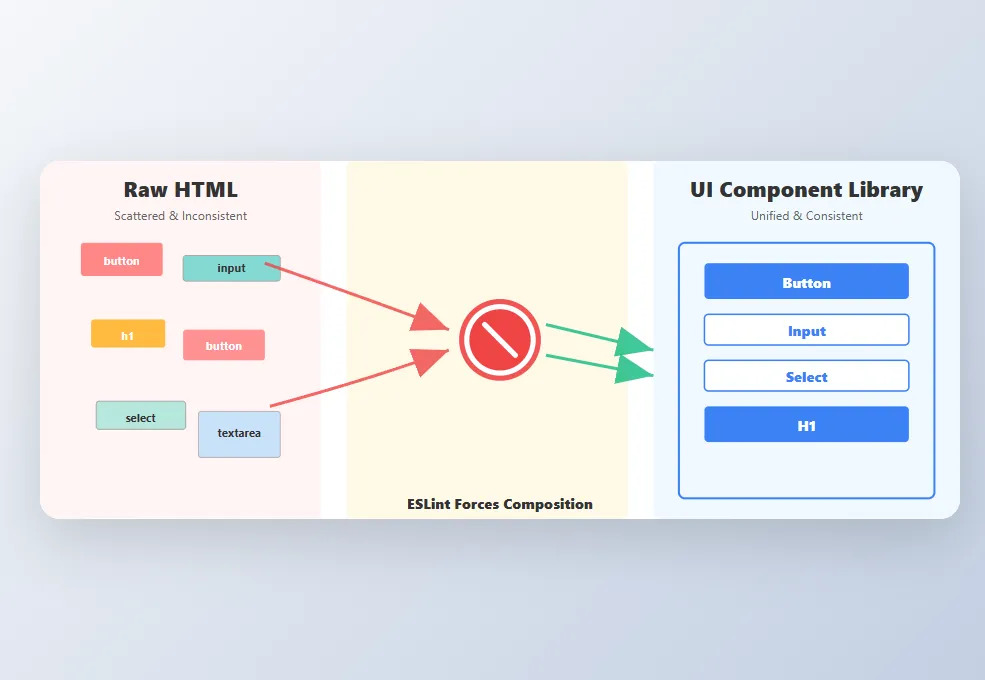
The Problem: AI generates inline HTML elements (<button>, <input>, <h1>) scattered throughout the codebase. When you need to adjust font sizes or shift color schemes, you're hunting through dozens of files with inconsistent styles. Worse—forgotten, abandoned components with conflicting styles linger, creating visual debt.
The Solution:
Create an ESLint rule that forbids raw HTML elements and forces composition from your UI component library:
// packages/eslint-plugin/rules/no-raw-html-elements.js
const FORBIDDEN_ELEMENTS = {
button: 'Button',
input: 'Input or PasswordInput',
select: 'Select',
textarea: 'Textarea',
h1: 'H1',
h2: 'H2',
h3: 'H3',
h4: 'H4',
h5: 'H5',
h6: 'H6',
}
export default {
meta: {
type: 'problem',
docs: {
description: 'Require UI components instead of raw HTML elements',
recommended: true,
},
},
create(context) {
return {
JSXOpeningElement(node) {
const elementName = node.name?.name
const lowerName = elementName?.toLowerCase()
const replacement = FORBIDDEN_ELEMENTS[lowerName]
if (replacement && elementName[0] === elementName[0].toLowerCase()) {
context.report({
node,
message: `Use <${replacement}> from @/components/ui instead of <${elementName}>`,
})
}
},
}
},
}Configure in your ESLint config:
// eslint.config.js
export default [
{
rules: {
'custom/no-raw-html-elements': 'error',
},
},
]Why This Works: When the AI tries to generate <button> or <h1>, ESLint immediately errors, forcing a refactor to your reusable <Button> or <H1> components. Now changing a button's padding, color, or font size updates instantly across your entire codebase—no hunting, no inconsistencies, no style drift. Your UI stays locked in.
10. Define Red Flag Patterns to Avoid
Negative examples are as powerful as positive ones. Tell the AI what NOT to do.
The Problem: AI repeats common anti-patterns.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Patterns to NEVER Use
❌ NEVER:
- `any` type (use `unknown` + type guards)
- `console.log` for errors (use `console.error`)
- Nested ternaries > 2 levels
- `setTimeout` for non-delay purposes
- Array index as React key for dynamic lists
- `eval()` or `Function()` constructor
- Hardcoded secrets/API keys
When tempted: explain WHY and propose alternative.For more on test integrity rules for AI agents, check out my previous deep-dive.
11. Establish Naming Conventions Explicitly
AI follows patterns it sees documented. Vague conventions lead to inconsistent naming.
The Problem: AI generates inconsistent naming across files.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Naming Standards
**Files:**
- Components: `PascalCase.tsx`
- Hooks: `useCamelCase.ts`
- Utils: `kebab-case.ts`
- Types: `PascalCase.types.ts`
**Variables:**
- Booleans: `is`, `has`, `should`, `can` prefix
- Handlers: `handle{Noun}{Verb}` (handleUserClick)
- Async functions: verb prefix (fetchUser, createPost, deleteItem)
- Constants: `SCREAMING_SNAKE_CASE`This pairs well with TypeScript and AI tools—strong typing plus consistent naming equals fewer bugs.
12. Create Skills for Repetitive Workflows
Stop repeating complex prompts. Encapsulate institutional knowledge into reusable skills.
The Problem: Repeating same prompts for common tasks.
The Solution:
# .claude/skills/create-api-endpoint.md
## Create API Endpoint
When user says "create endpoint for {resource}":
1. Create `src/app/api/{resource}/route.ts`
2. Add Zod schema: `src/schemas/{resource}.ts`
3. Add types: `src/types/{resource}.ts`
4. Create test: `__tests__/api/{resource}.test.ts`
5. Update docs: `docs/api.md`
[Include code templates for each file]Invoke with: /create-api-endpoint users
13. Implement Memory/Handoff Files for Session Continuity
AI sessions are stateless. Structured handoff files ensure the next session picks up exactly where you left off with clear context and next steps.
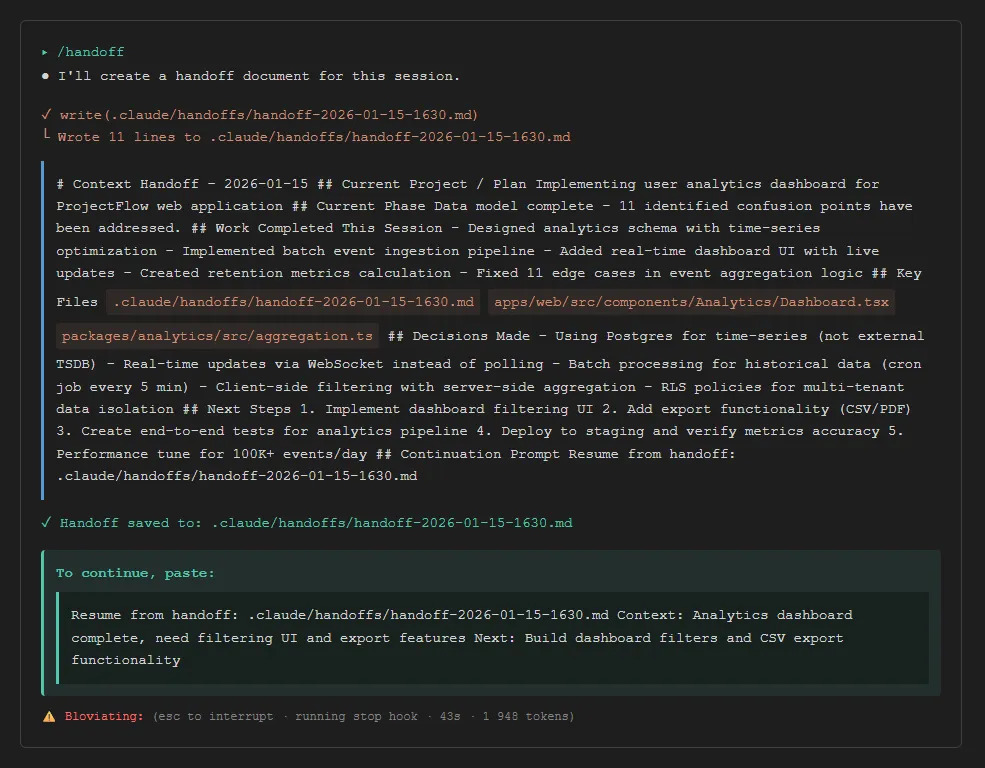
The Problem: New sessions lose all context from previous work, forcing manual context re-entry and wasting time.
The Solution:
Use a standardized handoff format. Save when context approaches capacity (10-15% remaining):
# Context Handoff - 2026-01-15
## Current Project / Plan
Building Medium publishing automation for jsmanifest blog
## Current Phase
Database schema complete, API endpoints in progress
## Work Completed This Session
- Created Supabase migration for medium_drafts table
- Implemented /api/admin/medium/generate endpoint
- Added RLS policies for draft access control
## Key Files
- supabase/migrations/002_create_medium_drafts.sql
- apps/web/src/app/api/admin/medium/generate/route.ts
- apps/web/src/components/admin/medium/DraftApproval.tsx
## Decisions Made
- Using React Query for draft state with 30s staleTime
- Storing Medium post IDs in RLS-protected table
- Webhook validation via Authorization header
## Next Steps
1. Implement draft approval UI
2. Add publish endpoint with error retry
3. Create end-to-end tests
4. Deploy with `supabase db push`
## Continuation Prompt
Resume from handoff: .claude/handoffs/handoff-2026-01-15-1430.mdTo continue in a new session, start with:
Resume from handoff: .claude/handoffs/handoff-2026-01-15-1430.md
Context: Building Medium publishing automation, database complete, need to implement approval UI
Next: Complete draft approval component and publish endpoint
Why This Works: The AI immediately has project context, knows what was completed, understands design decisions, and has a clear next action. No time wasted re-explaining or rebuilding context—you pick up in seconds.
14. Use Parallel Agents for Independent Tasks
Why wait for sequential execution when tasks are independent?
The Problem: Serial execution wastes time on independent tasks.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Parallel Execution
When tasks are independent, launch multiple agents:
✅ Parallelize:
- Linting + Type checking + Testing
- Multiple file reads for exploration
- Independent component implementations
❌ Don't parallelize:
- Sequential dependencies (create file → edit file)
- Tasks sharing state
- Order-sensitive operationsExample: "Run lint, type-check, and tests in parallel" triggers 3 concurrent agents.
15. Configure Model Selection Per Task Type
Not every task needs Opus. Match model capability to task complexity.
The Problem: Using expensive models for simple tasks wastes resources.
The Solution:
# CLAUDE.md - Model Selection
Use appropriate model for task complexity:
**Haiku (fast, cheap):**
- Simple refactors
- Formatting/linting fixes
- Boilerplate generation
- Quick lookups
**Sonnet (balanced):**
- Feature implementation
- Code reviews
- Bug investigation
- Documentation
**Opus (complex reasoning):**
- Architecture decisions
- Complex debugging
- Multi-file refactors
- Security auditsConclusion
These 15 strategies transform AI from "smart autocomplete" into an intelligent pair programmer. The meta-lesson? Treat AI configuration like code—version control it, review changes, iterate based on results.
If you're new to AI coding agents, start with strategies 1, 3, and 5 today. They'll give you the biggest immediate improvement. Add the others as you encounter their problems.
The developers who master AI configuration will have a massive productivity advantage in 2026 and beyond. The tools are here—it's about learning to wield them effectively.
And that concludes the end of this post! I hope you found this valuable and look out for more in the future!
Continue Learning: